The best automation equipment for plastic manufacturing starts with melt-system stability. Plastic molders added 1,646 robots globally in 2023, according to the International Federation of Robotics, yet melt instability often limits their full potential, pushing scrap rates higher and disrupting throughput.
With the U.S. plastics market projected to grow significantly, pressure on uptime, cost per unit, and on-time delivery rises. This guide covers top automation equipment from a melt perspective, focusing on components and data that support scrap reduction and stable cycles.
Key Takeaways
Stable automation depends on consistent melt quality and real-time machine feedback.
The screw, barrel, valve, and nozzle form the foundation of automation.
Melt monitoring provides live data for predictive service and automated corrections.
Precision hardware helps reduce scrap, improve shot consistency, and increase uptime.
Engineering-led component selection supports lower supplier risk and more stable production.
What Automation Equipment Means in Plastics Manufacturing
Automation equipment refers to tools that help your molding machine run stable cycles with less operator input. In plastics, this includes both downstream robotics and upstream melt-control components like screws, valves, sensors, and nozzles.
When the melt is stable, robots, conveyors, and inspection systems work with fewer interruptions and deliver more predictable throughput.
Why Hardware Problems Disrupt Automation?
Automation often focuses on robotics, fast tool changes, or part-handling systems. But on most molding floors, the biggest barrier to stable automation is not the robot.
Melt variability inside the screw, barrel, valve, and nozzle causes shot-to-shot changes. Even the best automated line struggles to maintain scrap, downtime, and cycle consistency.
Why This Matters for Daily Operations
Minor hardware deviations quickly impact measurable performance indicators like scrap rate, cost per unit, equipment uptime, and delivery reliability.
This positions the melt system as a strategic control point.
How Variability Impacts Your KPIs
The table below outlines how component wear, or failure, affects automation outcomes and how engineered melt solutions help stabilize performance.
KPI Impact Table
KPI | Effect of Component Failure | How Engineered Melt Components Support Stability |
Scrap Rate | Uneven melt temperature or mixing causes warpage and short shots. | Consistent melt flow helps reduce scrap variation. |
Equipment Uptime | Wear forces unplanned maintenance and machine stoppages. | Durable materials and geometry support longer run life. |
Cost Per Unit | Over-packing and energy waste increase unit cost. | Stable melt reduces cycle time and avoids excess material use. |
Lead Time Stability | Downtime disrupts production schedules and delivery commitments. | Predictable melt behavior supports tighter process windows. |
Note: As automation increases, melt instability has a larger impact because robots and downstream systems assume consistent part quality.
With the KPI effects clear, the next step is understanding how to create a stable melt system. This requires looking beyond general machine hardware and focusing on precision components that control resin behavior from the hopper to the mold gate.
What Helps Your Machines Work the Same Every Time

Most automation plans focus on robotics or auxiliary equipment, yet the melt system decides how stable each cycle will be. When the screw, barrel, valve, and nozzle deliver a consistent melt, automation becomes predictable.
But, when they do not, scrap rate, material usage, and uptime KPIs begin to drift. This section explains how engineered melt components support stable metering, controlled injection, and reliable automation performance.
1. Why Precision Plasticating Matters
A steady metering phase is necessary for automated molding. The screw, barrel, and non-return valve must work as a matched system to maintain uniform melt quality.
Key Functions That Influence Metering Stability
Heat transfer: The resin must melt uniformly without hot or cold spots.
Backflow control: Melt must not leak backward during injection, which affects cushion stability.
Mixing efficiency: Proper geometry helps maintain uniform viscosity.
Material compatibility: Geometry and metallurgy must support filled or sensitive resins.
Metering Stability Comparison Table
Component | Common Issue in Standard Parts | Impact on KPIs | Benefit of Engineered Option |
Screw | Uneven melting or poor mixing | Higher scrap and unit cost | Improved homogeneity supports consistent shots |
Wear at feed or transition zones | Pressure fluctuation and downtime | Longer service life supports better uptime | |
Check Valve | Backflow leakage | Cushion variation, weight instability | Positive sealing supports consistent metering |
Also Read: Melt Profiler Technology Spotlighted in Plastics Technology Magazine
2. The Nozzle's Role in Final Melt Control
The nozzle controls how the melt enters the sprue. Even a small leakage at this point affects part weight, mold cleanliness, and setup stability.
Why the Nozzle Matters in Automated Lines
It defines the final melt temperature entering the mold.
It affects drool and stringing, which influence scrap and rework.
It determines whether the sprue face stays clean across long runs.
It supports pressure control when the machine adjusts for viscosity shifts.
Common Nozzle Issues and Their Effect
Issue | Process Impact | KPI Impact |
Drool or stringing | Mold face fouling, inconsistent fill | Higher scrap rate |
Leakage at sprue | Flash or poor gate quality | Rework and downtime |
Temperature fluctuation | Short shots or burn marks | Cycle variation |
Poor shut-off control | Cushion drift | Shot-weight instability |
Note: A reliable nozzle helps protect downstream automation because robotic handling depends on consistent part quality at every cycle.
Stable hardware sets the foundation, but automation becomes truly reliable with real-time melt data. The following section explains how melt monitoring closes the loop between mechanical stability and automated decision-making.
Why Real-Time Melt Data Matters in Automation
Automation depends on fast detection and correction of variations. Real-time melt monitoring provides this visibility.
How Melt Monitoring Supports Automation
Sensors at the front of the barrel measure melt temperature and pressure. This data is used for predictive service and automatic adjustments.
What Real-Time Data Supports
Early detection of wear that affects the cushion and shot weight
Automated parameter corrections to maintain melt viscosity
Fewer defects caused by sudden temperature or shear changes
Better planning of maintenance windows
Internal Link Placeholder: [Explore Melt Monitoring Systems]
Real-time melt data reduces guesswork and helps the machine react before defects appear.
Once the melt conditions are stable and visible, the next step is to understand how automation systems fit together across the full production workflow. This context supports better equipment choices and more predictable operational results.
Key Automation Equipment Used in Plastics Manufacturing
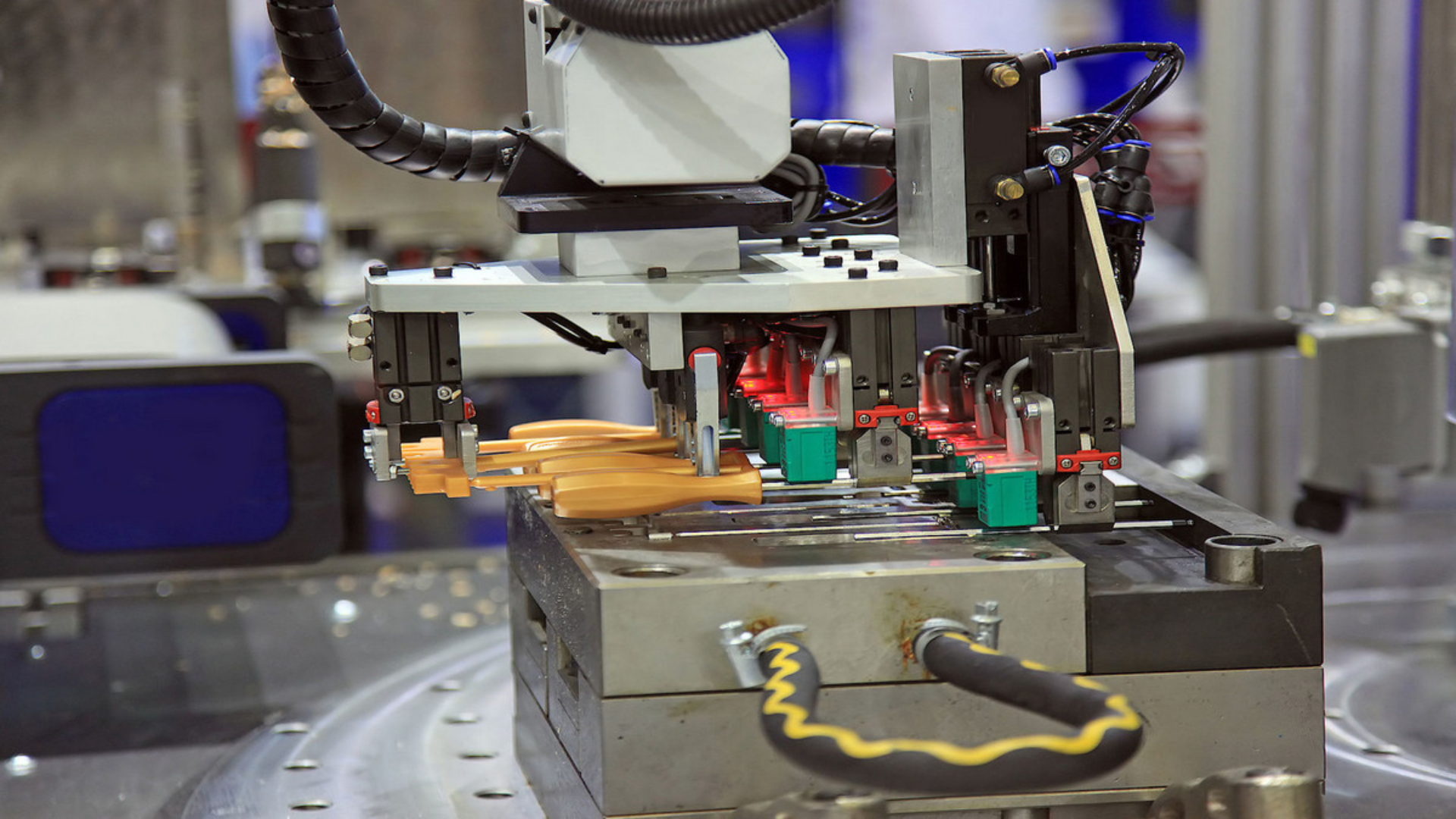
Every automated line depends on three categories of equipment: the melt system, the handling equipment, and the ancillary support. Understanding each category helps teams make informed choices that protect throughput, uptime percentage, and cost per unit.
This section outlines the main equipment groups and their role in automated molding.
1. Core Equipment Groups in Plastic Manufacturing
These equipment categories work together to manage raw material, melt preparation, and finished-part handling.
Primary Automation Categories
Category | What It Does | Operational Impact |
Melt Processing System | Heats, mixes, meters, and delivers resin to the mold | Sets melt consistency, supports stable cycles |
Part Handling & Robotics | Removes, places, trims, or assembles parts | Reduces labor and supports higher throughput |
Ancillary Equipment | Manages drying, loading, blending, and cooling | Supports material flow and reduces interruptions |
Note: Automated systems reach their full potential only when the melt entering the mold is predictable. This is why melt processing remains the first point of control.
2. Why Melt Processing Is the Base of Automation
Even advanced robots cannot compensate for inconsistent plasticating. Stable melt quality reduces rework, supports tighter tolerances, and keeps cycle times steady.
Key Melt System Responsibilities
Maintain uniform melt temperature
Support predictable viscosity
Provide stable back pressure during metering
Deliver a consistent flow into the sprue
Reduce contamination and degradation
These outputs help protect automated operations from cycle drift, part deformation, and mold fouling.
3. How Melt Processing Links to Downstream Automation
When melt consistency is unstable, the first observable impacts appear in downstream equipment.
Examples of Downstream Effects
Melt Instability | Impact on Automation | KPI Affected |
Hot/cold spots | Robot picks inconsistent parts | Scrap rate |
Cushion variation | Gate quality shifts | Yield improvement |
Drool at sprue | Mold fouling interrupts the robot path | Uptime |
Pressure fluctuation | Part weights drift | Cost per unit |
Understanding the key equipment categories helps clarify how each part supports automation. The next step is identifying which tools deliver the most impact on melt stability, scrap rate, and equipment uptime. These are the best automation systems for plastics manufacturing today.
The Best Automation Equipment for Plastic Manufacturing Systems

Automation relies on specific tools that help stabilize the melt, reduce manual work, and support predictable output. Below is a clear list of widely used automation equipment categories that improve throughput and reduce scrap.
Best Automation Tools and Equipment Used in Plastic Manufacturing
Equipment Type | Core Function | KPI Impact |
Melt Monitoring Systems (e.g., melt sensors) | Tracks melt temperature and pressure in real time | Lower scrap rate, steadier shot weight |
Automatic Shut-Off Nozzles | Prevents drool and melt leakage between cycles | Higher yield, fewer mold cleanings |
Precision Non-Return Valves | Provides stable metering and shot control | Better cushion stability and lower variation |
Custom Screws & Barrels | Improves melt homogeneity and reduces wear | Higher throughput, better energy efficiency |
Robotic Part Handlers | Automates ejection, trimming, and placement | Faster cycles, reduced labor cost |
Smart Material Dryers & Loaders | Controls moisture and blends material correctly | Lower defect rates for sensitive resins |
Automated QC Cameras & Sensors | Captures defects immediately after molding | Faster detection, lower rework rate |
Automated Mold Temperature Controllers | Maintains tight thermal profiles | Improved consistency and dimensional accuracy |
Conveying & Packaging Automation | Moves finished parts with minimal delay | Higher line efficiency and uptime |
Note: Melt-related tools deliver the greatest stability impact, because nearly all downstream automation depends on a consistent melt entering the mold.
Once you understand the core automation tools used across the plastics industry, it becomes easier to choose the right components. Modern plasticating systems are shifting toward intelligent, predictive control, which reduces manual intervention and improves long-term stability.
How to Choose the Right Components for Automation
Engineered component selection directly affects uptime, supplier risk, and long-term cost.
Checklist for Selecting Melt-System Components
Use this list when evaluating suppliers:
Do they offer resin-specific screw and barrel geometry?
Are materials suitable for abrasive or corrosive resins?
Does the valve design reduce dead spots and leakage?
Do they provide melt-system diagnostics or engineering support?
Can monitoring systems integrate into existing controls?
Resin compatibility?
Diagnostics support?
Key Differences Between Standard vs Engineered Components
Component | Standard | Engineered |
General geometry, shorter life | Resin-specific geometry, longer stability | |
Higher leakage risk | Designed for tight sealing and longer life | |
Open tip, drool risk | Automatic shut-off improves consistency |
A well-matched melt system needs fewer corrections. The next step is measuring its financial and operational impact using clear KPIs.
Measuring Automation ROI with KPIs

Automation only delivers long-term value when it improves measurable outcomes. This section explains how melt stability affects cost per unit, scrap rate, throughput, uptime, and supplier risk.
These KPIs help teams evaluate whether equipment choices are supporting or slowing automated performance.
1. Cost Per Unit and Scrap Rate
Stable melt quality lowers both material waste and energy consumption. Even small reductions in cycle drift or over-packing help reduce cost per unit in high-volume production.
How Melt Stability Affects Profitability
KPI | Problem Without Engineered Components | Improvement With Stable Melt |
Cost Per Unit | Over-packing increases resin use | A more uniform melt reduces excess material |
Scrap Rate | Warpage, short shots, splay | Better melt mixing lowers defect frequency |
Throughput | Unpredictable cycles slow automation | Consistent metering supports faster cycles |
Energy Use | Repeated corrections increase heater load | Stable melt temperature reduces energy spikes |
Note: Predictable melt behavior helps teams control process variation that directly raises cost per unit.
2. Supplier Risk and Uptime Stability
Automation breaks down when critical components fail, or when generic parts do not fit the machine or resin. Engineering-aligned sourcing helps reduce supplier risk and improves uptime percentage.
Key Considerations for Risk Reduction
Material compatibility for wear-heavy resins
Fitment accuracy for screws, valves, and nozzle tips
Predictable lead times for replacement parts
Technical support to diagnose issues before they reduce throughput
These points help minimize sudden stoppages that hurt uptime and lead time stability.
3. Maintenance and Changeover KPIs
Automated lines lose capacity when changeovers take too long, or when melt contamination slows startup.
How Engineered Melt Systems Help Operations
Area | Operational Issue | KPI Benefit |
Material Changeover | Dead spots cause contamination | Faster restarts improve uptime |
Wear Surfaces | Abrasive fillers damage internal components | Fewer rebuilds improve planned downtime ratios |
Thermal Consistency | Hot/cold zones trigger part variation | More stable cushions improve yield |
Note: Consistent melt systems improve both daily operations and long-term equipment planning.
With the impact understood, the next step is to see how automation varies by sector, each with its own demands on melt quality, part consistency, and equipment durability.
How Different Industries Use Automation
Different industries have different tolerance levels for variation. The melt system must align with sector-specific requirements.
Sector-Specific Melt Priorities
This table gives a clear context on how melt quality connects to product outcomes.
Sector | Core Requirement | Melt-System Focus |
Medical | Dimensional stability and cleanliness | Positive shut-off, controlled mixing |
Automotive | Strength and long-term reliability | Wear-resistant screws for filled resins |
Packaging | Fast cycles and low unit cost | Optimized geometry for throughput |
Aerospace | Processing high-performance polymers | High wear resistance and tight tolerances |
Note: As part complexity increases, the melt system requires higher engineering input.
The Future of Automation in Smart Plasticating and Predictive Service
Automation is shifting toward predictive systems that support autonomous operation.
Why Smart Melt Systems Matter
Real-time sensor data allows the machine to correct issues before defects appear.
Predictive Capabilities Supported by Melt Monitoring
Early detection of wear trends
Adjustment of heater bands and hold pressure
Consistent viscosity despite resin or temperature shifts
Note: These capabilities increase the stability of high-volume automated lines.
Conclusion
Automation succeeds when the melt is consistent. Precision plasticating components, stable valves, reliable nozzles, and real-time melt monitoring form the base of a predictable automated process. When these systems work together, plants gain measurable improvements in scrap rate, cost per unit, uptime, and delivery consistency.
If you want to upgrade your melt stability with minimal disruption, you can contact MD Plastics and review available engineered melt-system components that fit your machines and materials.
FAQs
1. What is the best automation equipment for plastic manufacturing when melt stability is the main issue?
The most effective tools are melt monitoring systems, precision non-return valves, and automatic shut-off nozzles, because they stabilize the melt before automation takes over.
2. Which automation tools help reduce the cost per unit in injection molding?
Custom screws, engineered check valves, and smart dryers help control energy use, reduce over-packing, and support shorter, more stable cycle times.
3. Do robots alone qualify as the best automation equipment for plastic manufacturing?
No. While robots assist with part handling, melt-side tools such as shut-off nozzles and melt sensors have a larger effect on part consistency and automated line performance.
4. What should I evaluate before selecting automation equipment for plastics processing?
Check melt stability needs, resin type, cycle targets, uptime requirements, and whether equipment suppliers offer engineering support for your full melt system.